Having a Terms and Conditions agreement for your SaaS app can help you control your app better, while at the same time limiting reasons why your users can bring legal action against you. It's a crucially important legal document for every SaaS app to have.
This article will explain exactly what a SaaS Terms and Conditions agreement is, why having one is so important, and help explain what it should include. We've also created a Sample SaaS Terms and Conditions Template, which you can download to assist you in drafting your own.
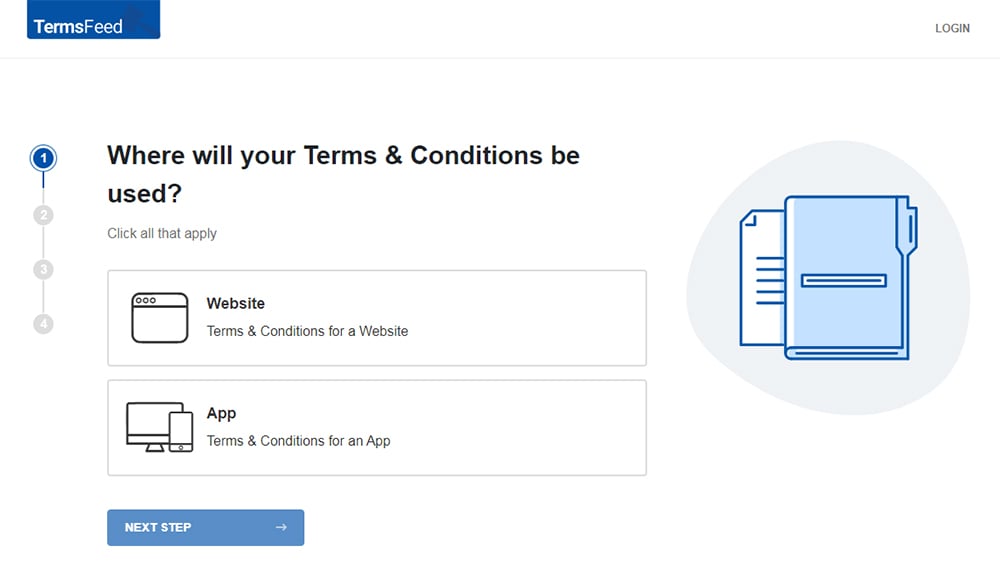
Our Terms and Conditions Generator makes it easy to create a Terms and Conditions agreement for your business. Just follow these steps:
-
At Step 1, select the Website option or the App option or both.
-
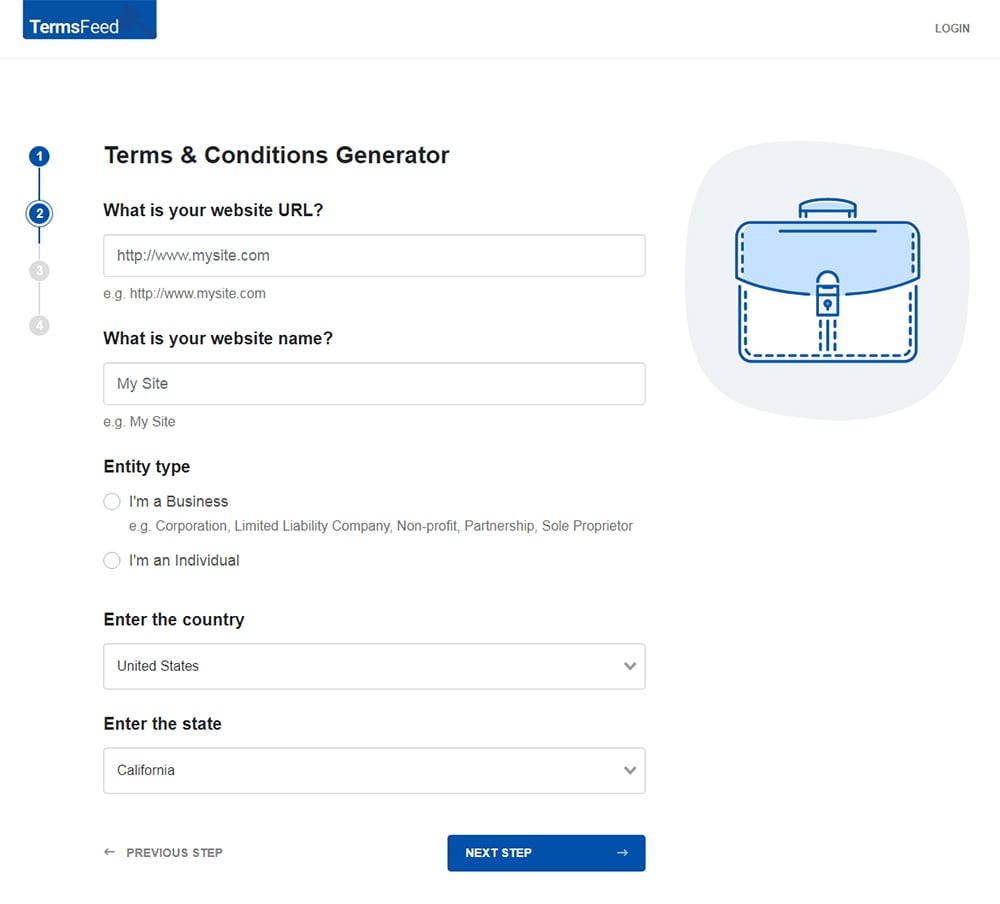
Answer some questions about your website or app.
-
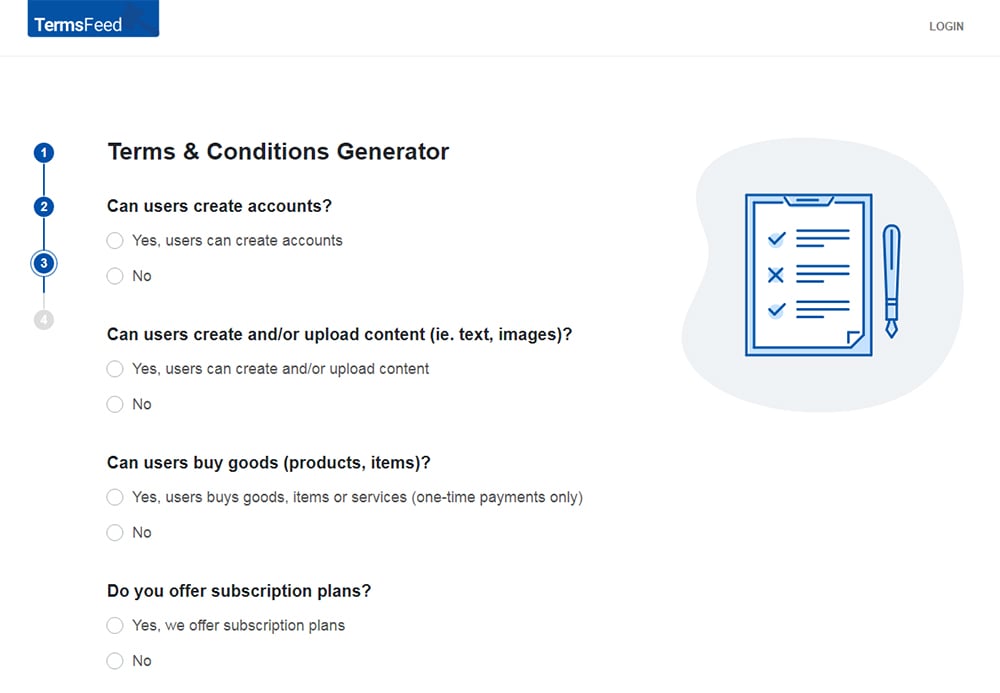
Answer some questions about your business.
-
Enter the email address where you'd like the T&C delivered and click "Generate."
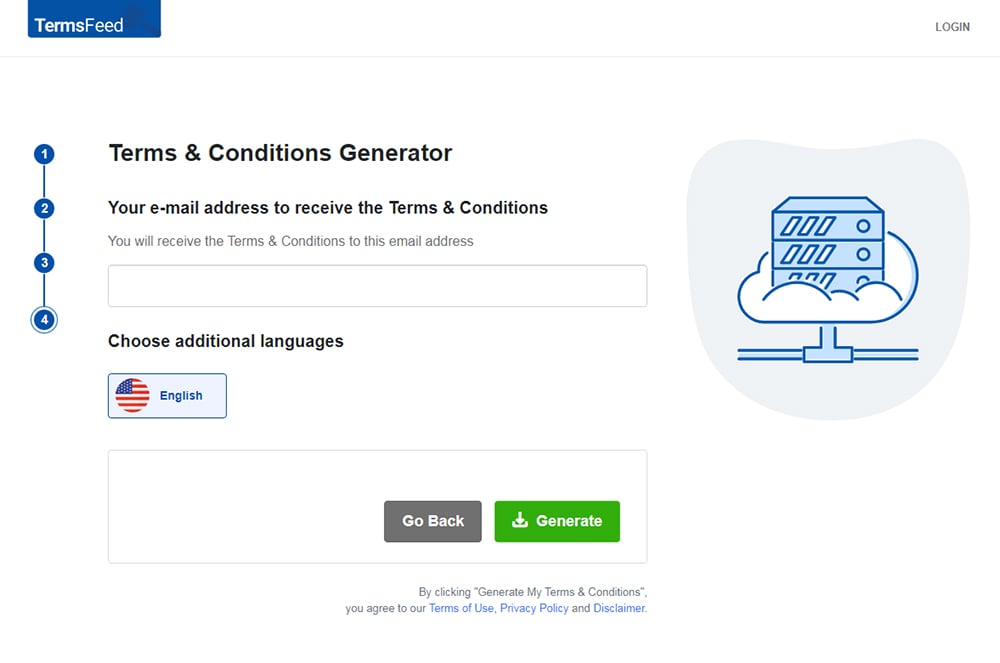
You'll be able to instantly access and download the Terms & Conditions agreement.
- 1. What is a Terms and Conditions Agreement?
- 2. Why Do SaaS Companies Need a Terms and Conditions Agreement?
- 3. Are Terms and Conditions Agreements Legally Required?
- 4. Clauses for SaaS Terms and Conditions Agreements
- 4.1. Acceptance of Terms
- 4.2. Licensing Information
- 4.3. Copyright Protection
- 4.4. User-Generated Content
- 4.5. Intellectual Property
- 4.6. Termination of Accounts
- 4.7. Governing Law
- 4.8. Links to Other Websites
- 4.9. Allowed and/or Prohibited Uses
- 4.10. Privacy Policy Information
- 4.11. Limitation of Liability
- 4.12. Disclaimer of Warranties
- 4.13. Changes to the Terms
- 4.14. Fees, Payments and Refunds
- 5. Displaying Your SaaS Terms and Conditions Agreement
- 6. Getting Agreement for Your SaaS Terms and Conditions Agreement
- 6.1. Getting Agreement: Accounts Created on Website, Not via App
- 7. Summary of a SaaS Terms and Conditions Agreement
- 8. Download Sample SaaS Terms and Conditions Template
- 8.1. Sample SaaS Terms and Conditions Template (HTML Text Download)
- 8.2. Sample SaaS Terms and Conditions Template (PDF Download)
- 8.3. Sample SaaS Terms and Conditions Template (Word DOCX Download)
- 8.4. Sample SaaS Terms and Conditions Template (Google Docs Download)
- 8.5. More T&Cs Templates
What is a Terms and Conditions Agreement?
A Terms and Conditions agreement is where you set the rules and guidelines that your customers must follow in order to access the service you provide as a SaaS app. It acts as a legally binding contract between you and your customers. It lays out the conditions of use for the service, including things like copyright restrictions, rules for interacting with other users on the website/app, and dispute resolution procedures.
Note that there's no practical difference between a Terms and Conditions agreement, a Terms of Use and a Terms of Service agreement aside from the names. It may even be called an End User SaaS Agreement (EUSA). The name isn't as important as the content is.
Spotify calls it a Terms of Use:

Why Do SaaS Companies Need a Terms and Conditions Agreement?

With a proper Terms and Conditions agreement in place, a SaaS company can set expectations, retain control, and mitigate the possibility of any misuse of its services.
Here are just a few ways that having a Terms of Use for your SaaS app can benefit you:
-
If a paying customer starts spamming other users from your app, you can terminate the spammer's account based on the Terms and Conditions they agreed to.
A Termination clause in your Terms agreement can inform users that abusive behaviors will not be tolerated and that accounts of abusive users will be terminated at your sole discretion.
-
If users start posting content that they do not own rights to and this content is made public online, you will reserve the right to remove that content if it infringes copyright.
- The Terms and Conditions agreement would inform users what laws and regulations apply (between you and your customers) through a Governing Law clause.
Most likely, you have guidelines and rules in place to make sure that users interact with your service in a way that isn't harmful. These rules and guidelines are typically outlined in a Terms and Conditions agreement. You should consider this contract your friend. It safeguards your reputation and allows you to set your rules and restrictions.
Whether you're a Software as a Service (SaaS) startup launching your first product or your company has been around for a while, it's essential to understand the importance of having a SaaS Terms and Conditions agreement.
Those who don't have a Terms and Conditions agreement or don't include the proper clauses may find themselves in legal disputes that they might have otherwise avoided.
SaaS Terms and Conditions agreements will often include elements/clauses that are unique to SaaS agreements in addition to all the clauses that standard Terms and Conditions agreements contain.
For example, most Terms and Conditions agreements will have a section that covers rules of conduct while users are on the website or app, the use of content (copyright), and rules associated with the suspension or cancellation of a user's account. A SaaS Terms and Conditions agreement may also include information on its license agreement, reseller agreement, and subscription agreement.
Additionally, some may even contain a Service Level Agreement (SLA) that defines the service level a customer can expect, the metrics through which they are measured, and any available remedies if the company fails to meet these expectations.
See how Adobe provides information in its Terms of Use on subscriptions to its services in the screenshot below:

Terms and Conditions agreements are the perfect place to put Information such as this, as your users will know to look there for such things.
Are Terms and Conditions Agreements Legally Required?

Terms and Conditions agreements are not required by law. It's completely optional to have one for your SaaS app, but it's strongly recommended to have one.
In contrast with Privacy Policies, which are required by laws like the GDPR, CalOPPA, and many others, there's no law or regulation that demands businesses write and display a Terms and Conditions agreement.
With that said, it's still a best practice because Terms and Conditions agreements are advantageous to all businesses.
For instance, there are several different ways that a correctly written agreement can help your business:
- You can terminate an account if users misuse your website or mobile application in any way. If they abuse your service, you can use the Terms and Conditions agreement's Termination clause to terminate the abusive user's account.
- You can use your Terms to inform users that they can upload content to your website or mobile application (create content, share it on your platform), but you have the right to remove any content they make if it violates copyright. If users register for an account and select a username, you can tell them that any usernames they choose are not allowed to infringe on anyone's trademarks (e.g., usernames such as Google or Facebook are not allowed).
- You could add a clause in your Terms and Conditions to notify users that you can cancel certain orders if pricing is incorrect.
Clauses for SaaS Terms and Conditions Agreements

Standard Terms and Conditions agreements usually have sections that contain clauses on the following:
- Acceptance of terms
- Copyright information
- Intellectual property
- Termination clause
- Governing law
- Links to other websites disclaimer
- Content clause
- Allowed and/or prohibited uses clause
- Disclaimers and warranties
- Changes to terms
However, SaaS companies may wish to add the following clauses and sections to their Terms and Conditions agreements:
- Licensing information
- Reseller agreement
- Subscription agreement
- Fees and payment
Let's look at these clauses and see why they are important.
Acceptance of Terms
Include a statement early on in your Terms agreement that lets users know that the agreement contains terms that they need to accept in order to use your SaaS app. While this statement alone does not mean that a user is giving consent, it's standard practice to let users know that the Terms document is an agreement between them and you.
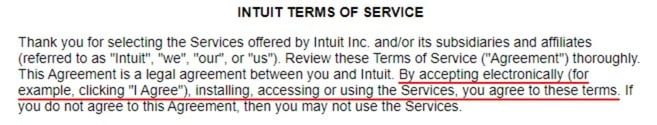
Here's how Intuit, an American financial software company with Saas products, words its Acceptance of Terms clause:
Licensing Information
A licensing clause permits your users to use your services only for a specified purpose. You will need to outline the following:
- The ways that a user can use your service
- Any license restrictions
- Any trademarks or intellectual property you wish to protect
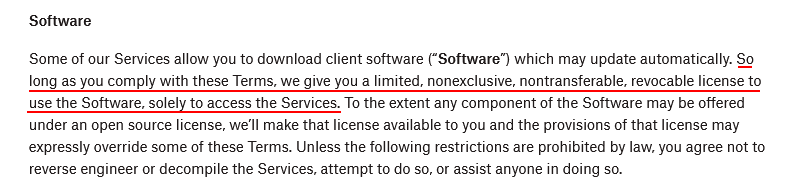
Dropbox gives users of its software products a limited license to access its services as seen below:
Copyright Protection
If your website or app allows users to share content or user-generated content, you must provide a way to report copyright infringement. This information can be included in your Terms and Conditions by adding a Copyright Infringement clause.
Here's how Dropbox addresses this in its Terms of Service:

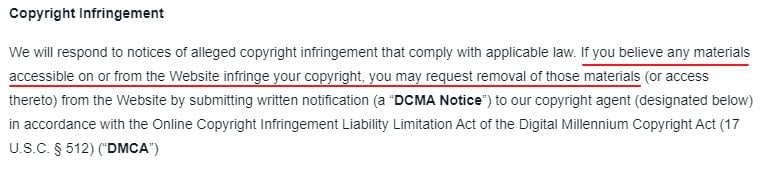
The Digital Millennium Copyright Act (DMCA) in the United States contains provisions that can make businesses liable for copyright infringement, even if they weren't responsible for posting the content themselves. This can be in your Terms and Conditions agreement as a DMCA clause.
You can avoid this liability by providing a mechanism for third parties to report violations.
This is how ServiceNow writes its Copyright clause to include DMCA information:
User-Generated Content
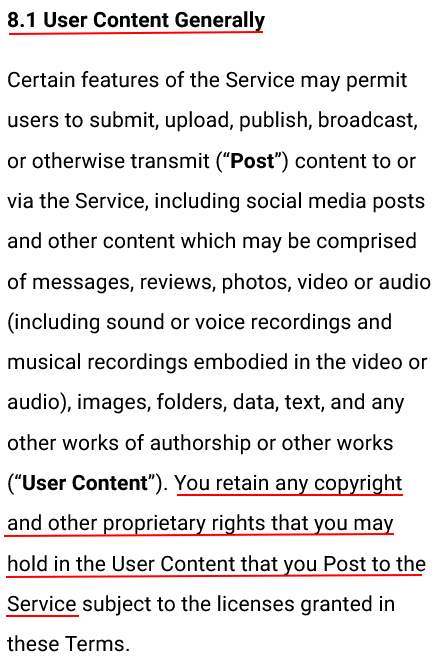
If your SaaS app allows customers to upload content - pictures, text, documents, videos, audio and so on - you should address copyright, intellectual property and any limited licenses you wish to reserve in the user-generated content.
Buffer lets users know that they retain any copyright and proprietary rights in their content:
Before you can use any of this content, you need to obtain a license from your users for your app to use that content. A way to do this is to add a clause to your agreement that explicitly states that your users gives you this license.
Basically, your users grant you a license to use and display the content they create on our platform. Since they created that content, they own it, but they're granting you permission to use that content.
Here's how Buffer grants itself a license to do certain things:

If Buffer didn't disclose this, the company would surely run into legal problems if it started using user content for such wide-ranging purposes as it reserves.
It's important to include both of these parts in your Terms and Conditions agreement:
- What copyright protection users have in their own content, and
- What licenses or rights you reserve to use their content for limited purposes
Intellectual Property
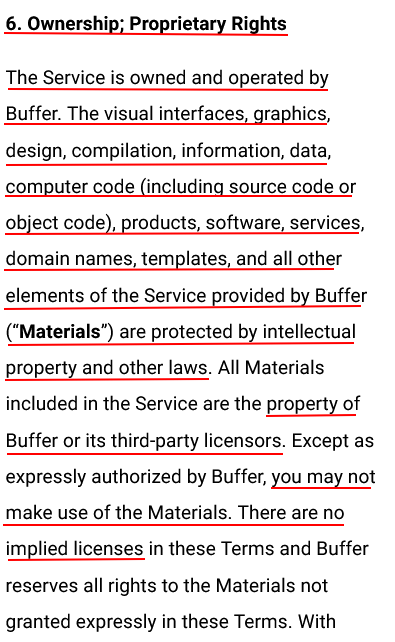
A clause addressing intellectual property will help you protect your IP by stating what property is yours and what rights you reserve in it. It informs the user that they cannot use your property without your permission.
Here's an example from Buffer that shows the declaration of what property is protected, and how it's protected (it can't be used without permission):
Unlike the DMCA, the "Intellectual Property Rights" clause in a Terms and Conditions agreement focuses on your own intellectual property.
Copyrights, trademarks, and proprietary information are all legally protected. This is crucial because users can easily download your logo and graphics by clicking the right-click button and then doing with it what they want.
Here's another example of such a clause from ServiceNow:

Termination of Accounts
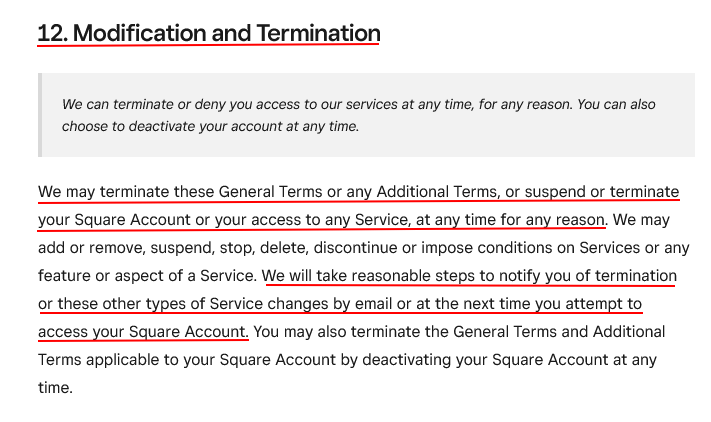
A termination clause is often included in a Terms and Conditions agreement to reduce liability. It explains how users can voluntarily delete their accounts. It also details circumstances where the company will terminate a user's account unilaterally. The notification process for account termination is often described in this clause.
Square makes it clear that it maintains the right to terminate a user account for any reason whatsoever:
The next clause in the agreement goes into futher detail about what the effects of termination are, including obligations of the user, what the company may do, and limits in liability:
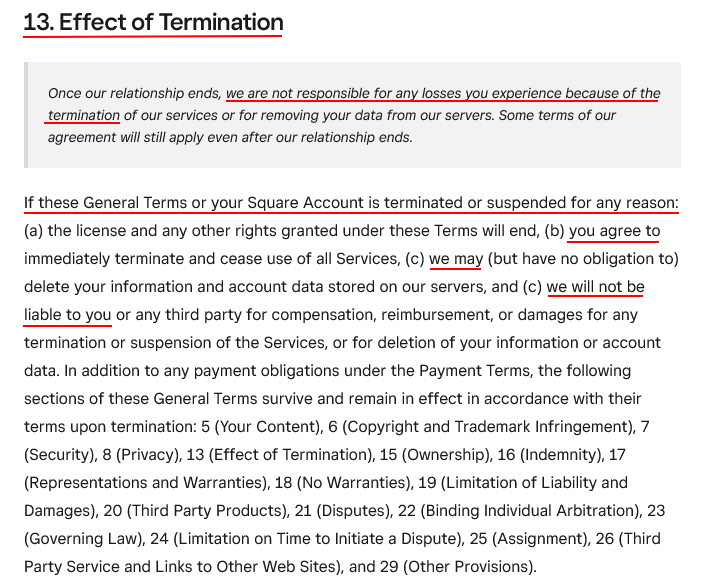
SurveyMonkey has a very detailed clause that outlines how accounts can be suspended or terminated, and what the results of such will be.
One section discusses how users can terminate their own accounts and what repercussions that has on account access and data. Note that this is just an excerpt of the full clause:

In a separate section of the same clause, SurveyMonkey also addresses how it can cancel or suspend user accounts, how it will do so, and what that will mean for users:

Governing Law
The governing law clause is a section in your Terms and Conditions agreement that dictates which jurisdiction's laws will be applied when it comes to any disputes between the parties involved in the agreement.
As your service may be used around the world, it's important to clearly state which country's law will govern the contract.
There are two parts to these provisions: governing law (the law that will be used to decide the dispute) and jurisdiction (where the dispute will be decided).
The jurisdiction is usually in the country or state where the business is based.
Governing law is different:
- Usually, if you're in Australia, you'll want your section to say that Australian law applies
- Or, if you're based in California, you would want the Californian law to apply. However, sometimes the law in another state in the U.S. is more favorable to businesses, such as Delaware.
Courts usually look for some connection between the business owner or the customers, and the state or country that has been chosen as governing law. Another factor is that cases looking at corporate behavior (i.e. if you are being sued), they must usually be decided in the state of incorporation.
It's also important to state that your legal agreement is the only contract between you and your users.
Here's an example of a governing law clause from Steelcase:

Here's another example from DataDog that shows its Terms are governed by the state of New York:

This clause is essential because it can help to avoid potential conflicts down the road by choosing a jurisdiction whose legal system with which you're comfortable.
Here's how Dropbox does this in a Controlling Law clause:

SurveyMonkey discloses the governing law as well as the jurisdiction and its legal name in a clause:

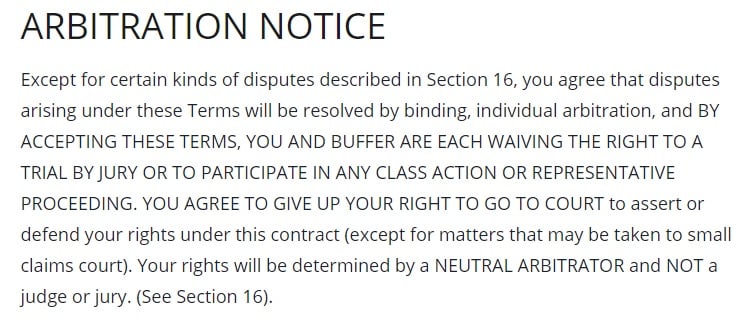
If you want to limit legal actions to arbitration, you'll need to include this in your Terms of Use, as such:
Links to Other Websites
In general, you should have a clause about links in your Terms and Conditions agreement to guard against any potential legal issues that could arise from users accessing other websites from yours.
Square ensures that users know they visit other sites accessed through links on its website at their own risk:

Allowed and/or Prohibited Uses
This clause should limit or prohibit certain activities on your website or app. While some of these prohibitions will be obvious (for example, no illegal activity), others may not be as apparent (for example, you don't want users spamming people).
You should decide what things you won't allow.
For example, you may wish to prohibit:
- Violations of the law
- Abusive behavior
- Anything that could put your company's reputation or intellectual property at risk
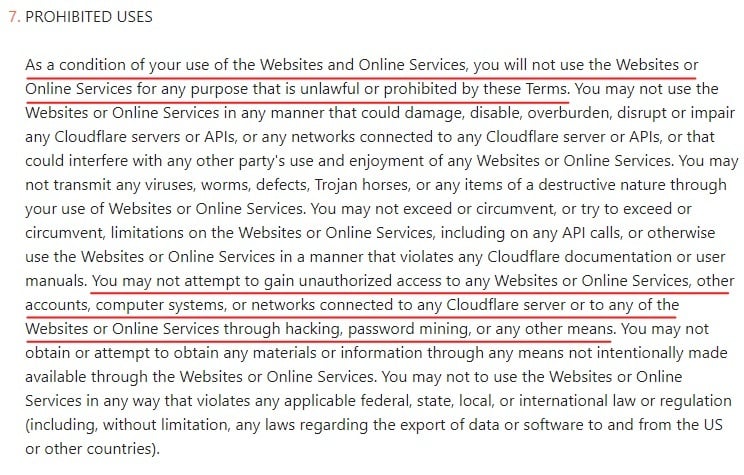
Here's how Cloudflare writes this clause:
Here's an example of Dropbox's Acceptable Use Policy page. Note that this is just an excerpt:

Dropbox has included a list of all of the types of behavior that it doesn't allow or accept.
Consider which of the above may apply to your app and which things a user might be able to do.
Either list out the types of misconduct in your main Terms and Conditions, or create a separate Acceptable Use Policy to cover these points.
Privacy Policy Information
Don't forget to include a Privacy Policy as well as most SaaS apps will need the Privacy Policy agreement. You need to make sure that the "Privacy" and the related cloud storage clauses clearly outlines what information will be kept by the app.
Your Privacy Policy should contain, at minimum, the following information:
- The types of information that you will collect
- How you will collect the information
- How you will use the information
- How you will keep it secure
- Whether any third parties who will be accessing the information on your behalf (e.g. cloud storage provider)
Limitation of Liability
One of the great benefits of having a Terms and Conditions agreement is that you can limit your legal liability through the agreement simply by stating that you aren't to be held liable for certain things and under the law. These clauses are very standard and tend to limit all liabilities to the fullest extent under the law.
Here's how Cloudflare includes a standard Limitation of Liability clause in its Terms agreement:

One of the legal issues that you need to consider is how you will keep your users' information secure, particularly if you are using a third-party cloud storage vendor, like Amazon AWS.
When your users sign up to your service, your app will collect information about them that will be stored either by a cloud storage service that you run or by that external provider.
But what happens if that external provider has a data leak? Who is responsible to your users, you or them?
![]()
Here's an example from the the Terms of Use of Amazon Cloud Drive:

Like Amazon, most cloud storage services do not guarantee that user data will be kept and limit their liability in the case of a loss.
If you are using an external cloud storage service to keep user data for your app, make sure that you notify your users of these risks in your Terms of Use agreement, and limit your liability so that you are not responsible for any loss of data caused by the cloud storage provider.
Disclaimer of Warranties
A disclaimer of warranties is a clause that basically states you do not warrant that everything will be flawless, and all of the time. Same as clauses that limit liability, these clauses tend to be fairly standard and the same from one agreement to the next with very minimal customizations.
Your business could theoretically be at risk of liability if, say, your website or app happened to go down and wasn't available for a brief time. In a scenario like that, this clause can help prevent you from being liable for any business damages the downtime caused for others using your service.
Splunk lets users know that all use of the site is at the user's own risk:

You could add language saying that you can't guarantee your services will always be available or in working condition. This is much the same as saying that the user can access services "as readily available."
Changes to the Terms
In this clause, you reserve your right to change or modify your Terms at any time. You can also let users know how you will notify them of any material changes you do make to your terms, such as via email or banner announcements on your website.
Although it might seem obvious to you, it could be a liability for your business if users expect that the Terms and Conditions will never change.
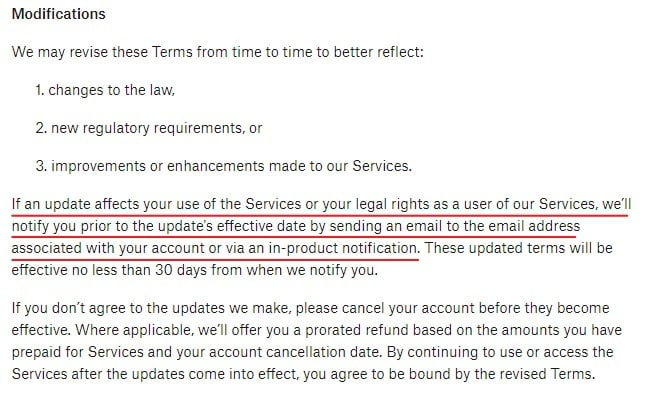
Here's how Dropbox writes its Modifications clause:
When SurveyMonkey updates any of these clauses or makes changes to its services, it's covered by the following clauses that reserve the right to make the changes. Users are also told how they'll be notified of any relevant changes:

Fees, Payments and Refunds
Most SaaS products run on some type of subscription service. If that's the case for yours, then you can add information in your Terms and Conditions agreement that addresses the following:
- What your fees are
- When payments are charged/billing information
- How users can pay and what methods of payment you accept
- How you handle refund requests
The first example that we'll look at is from HubSpot's Terms of Service. It includes information on subscriptions, renewal price increases, how invoices work, and how payment information is stored:

Basecamp has a clause that very clearly and briefly summarizes how it handles payments, refunds and plan changes:
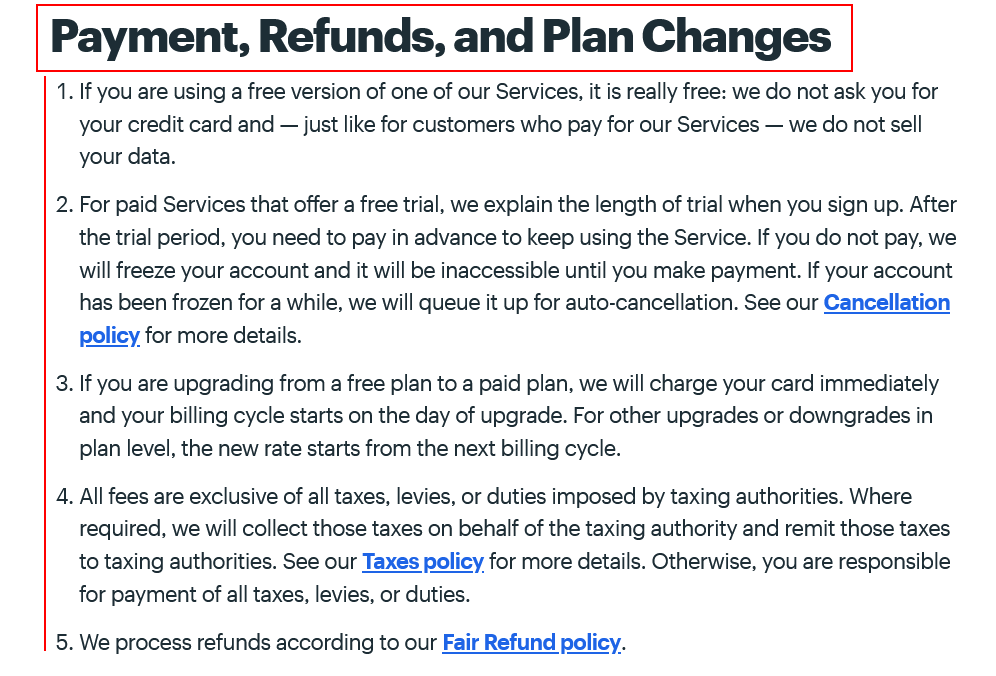
Now let's take a look at this example from Kissmetrics' Terms of Use that covers a wide range of topics in a nicely organiced, rather short clause:
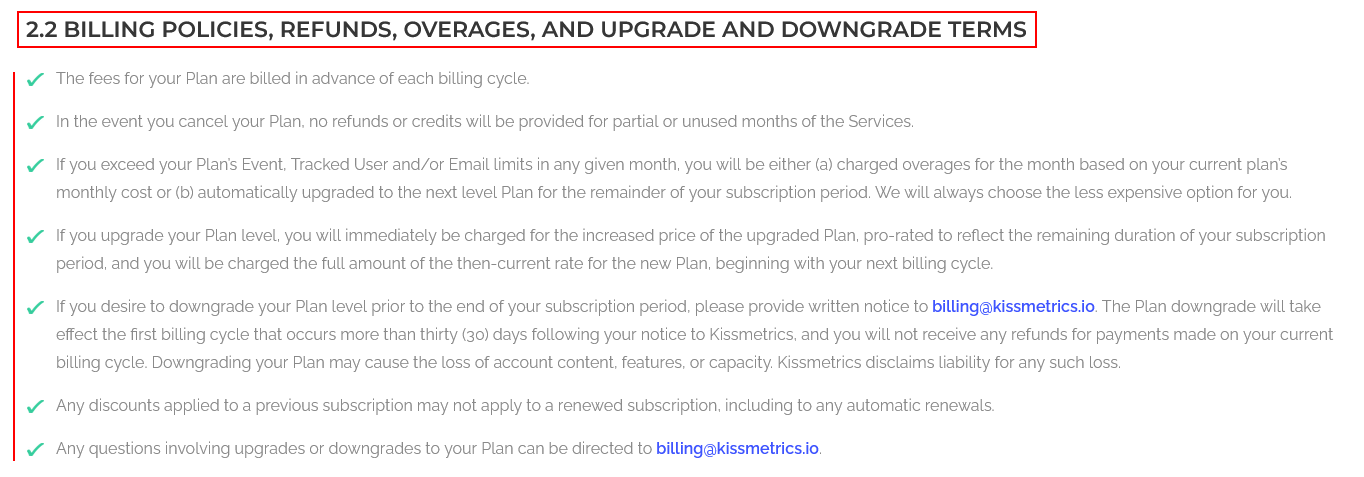
In a separate clause, Kissmetrics deals with free trials, their expiration, and upgrades from a free trial to a paid subscription:
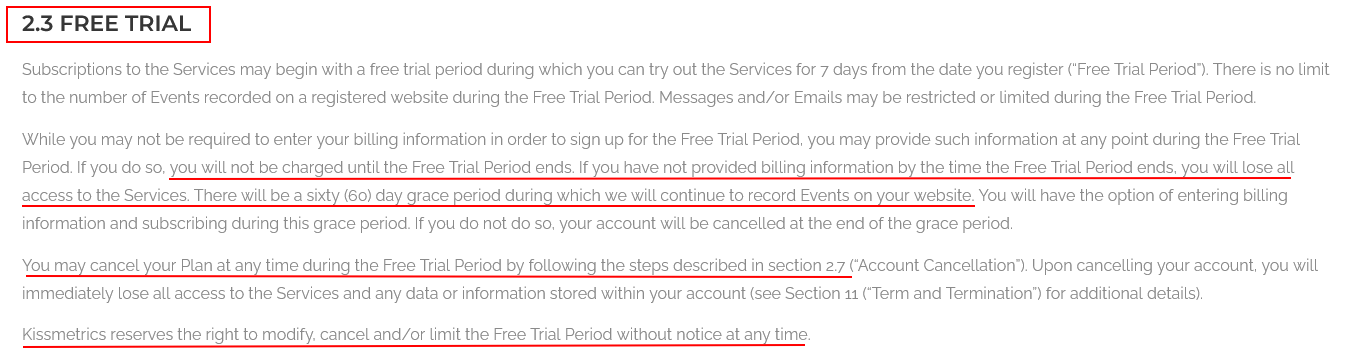
It's important to set out clearly in your Terms of Service agreement how free trials are managed and ensure that you don't forget to specify a time length for the trial.
Also specify how free trials can be changed into paid subscriptions, and how billing is effected. In the Kissmetrics' example above you can see that all that's required is that the billing information must be entered.
Don't forget to provide information on how your users can cancel their subscription. This helps to create user trust and ensures that users don't feel trapped or like they need to search to find how to stop using your service.
Like the information on your different subscription levels, information on cancellations should be clearly displayed on your main website.
Now that you know what you should put in your SaaS Terms and Conditions agreement, let's take a look at how you can get your users to agree to it. Without agreement, you cannot enforce your Terms and Conditions.
Displaying Your SaaS Terms and Conditions Agreement

It's important to display your Terms and Conditions agreement in a conspicuous location on your website in order for everyone to see it, know it exists, and have access. If you bury the document somewhere on your website that's hard to find, you could harm your case during mediation or legal disputes.
Another reason to make sure it's placed in an obvious location is that it makes it easier for you to obtain the necessary consent to your Terms.
You should include a link to your Terms and Conditions on the account registration page. Most companies also place a link to their Terms and Conditions agreement somewhere in the website footer, which users will see on every page.
Box provides a link to its Terms of Use in the footer of its website, along with other legal and important links:

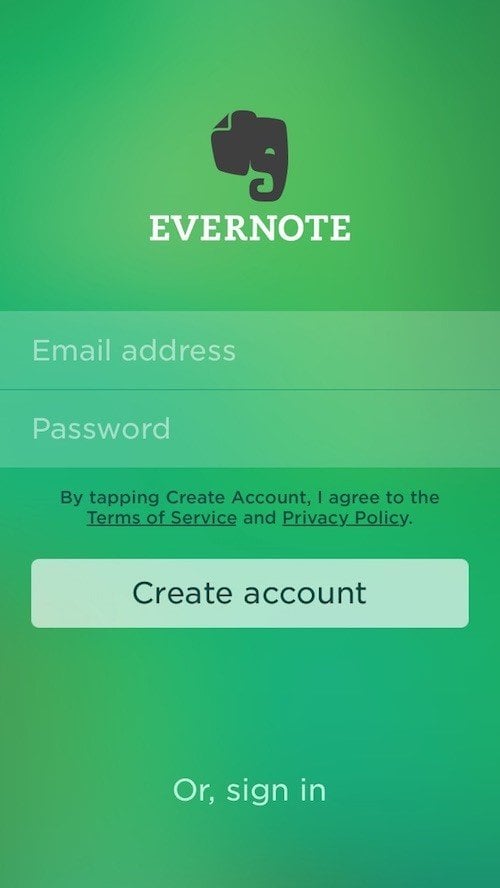
Evernote users can create an account through Evernote's website or mobile app. On the mobile app, users are informed that by tapping "Create account," they'll be agreeing to the Terms of Service agreement and Privacy Policy:
The same method was used for on Evernote's website, at the place where users can register for an account:
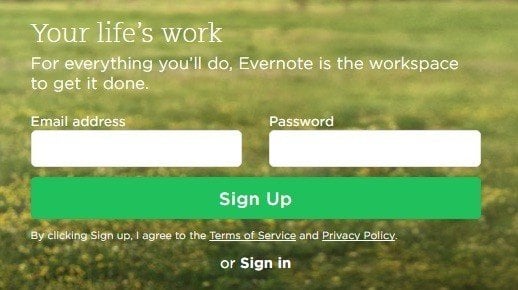
Make sure your Terms and Conditions link is available at any time when a user wishes to view it or you will have issues trying to enforce it.
Getting Agreement for Your SaaS Terms and Conditions Agreement

You must get users to consent to or agree to your Terms for it to be legally enforeable against them if ever needed. The best way to do this is with clickwrap, or an "I Agree" checkbox, like so:
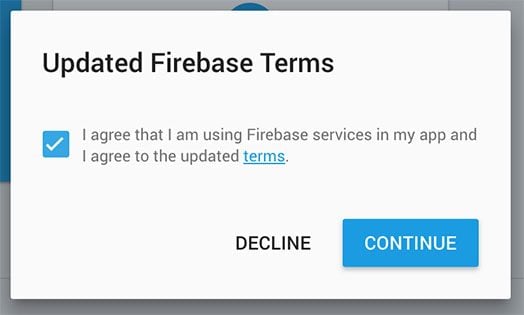
The term clickwrap describes the highly favored method of "click to accept" which gets your users to agree to your legal agreements by taking some action such as clicking a box or button next to a statement that makes it clear that clicking means agreeing.
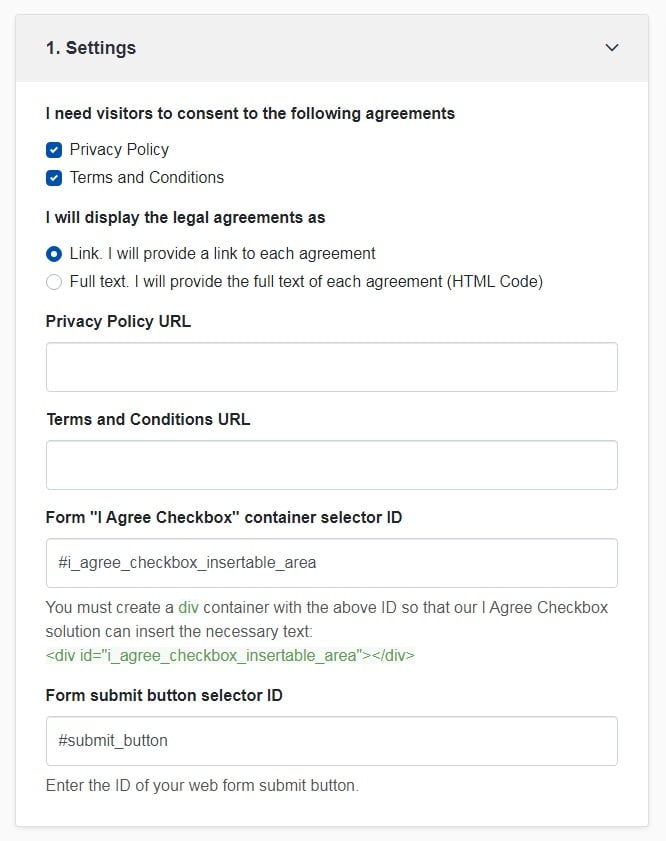
"I Agree" Checkbox by TermsFeed tool can help you enforce your legal agreements in 3 easy steps.
-
Step 1. Adjust the settings in order to display your legal agreements properly.
-
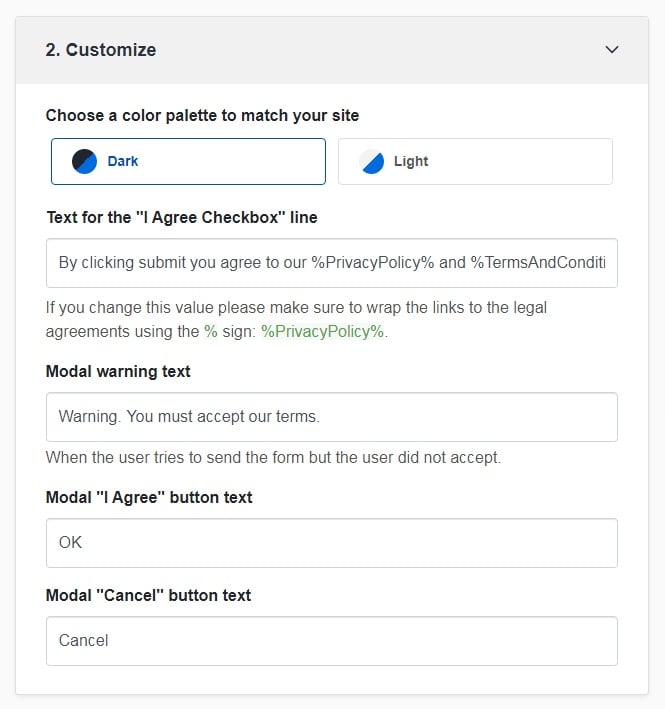
Step 2. Customize the style to match your brand design.
-
You're done! Just copy the generated code from Step 3 and copy-paste it on your website.
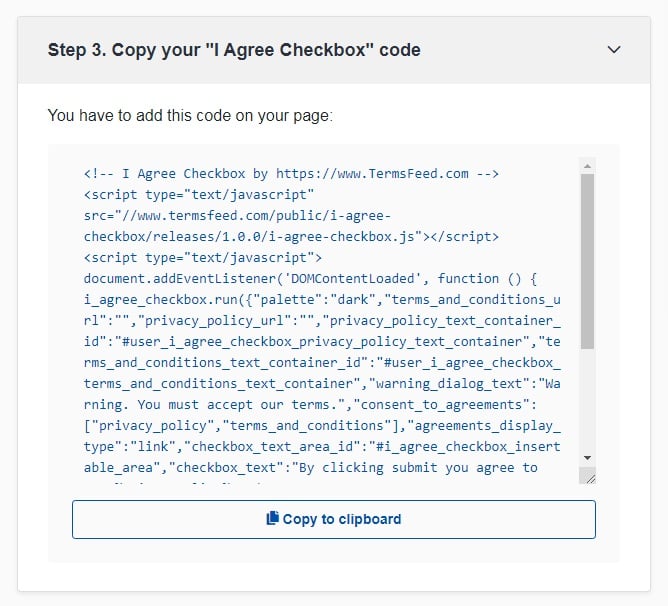
Clickwrap is by far the most popular and most recommended method because it leaves very little room for doubt that an agreement to various terms, rules, and guidelines have been formed between the business operating the application and the customer.
This is especially true for SaaS applications where business owners license the customer to use the application. Various legal agreements will allow that business owner to set restrictions of use or limitations of the licensing granted to the customer when using the applications.
If you're considering implementing clickwrap for your SaaS application, it's important to design your application/official website to make sure you obtain actual and clear intent from users to agree to be bound by the legal agreements before they access and use your application.
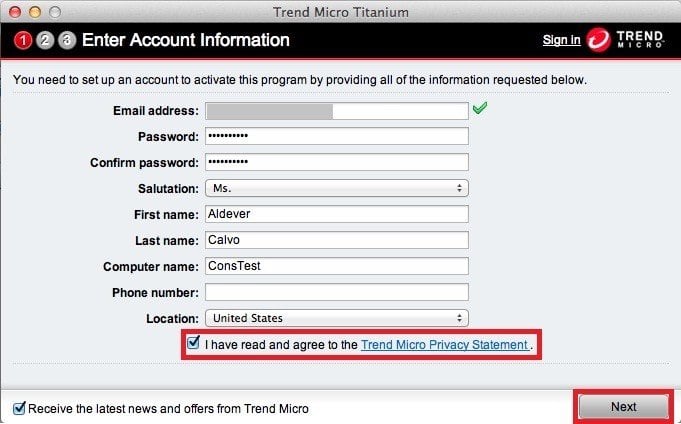
Have a look at this example below from TrendMicro application. While the TrendMicro's example is not a SaaS application, this example is good to showcase how clickwrap is usually implemented, regardless of the medium (website, mobile application etc.) or business model (SaaS, e-commerce etc.): a check box and informative text that says "I agree to ... "
Before proceeding with an account setup and clicking the "Next" button, a user must first click the check box that states that "I have read and agree to the Privacy Statement."
In the image below, the user must tap multiple boxes to agree to different legal agreements before being able to continue with creating a Samsung account:
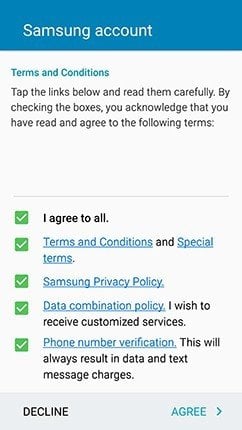
This example of Samsung implementing clickwrap on its mobile app showcases how SaaS applications can use clickwrap if they also offer a mobile application to customers.
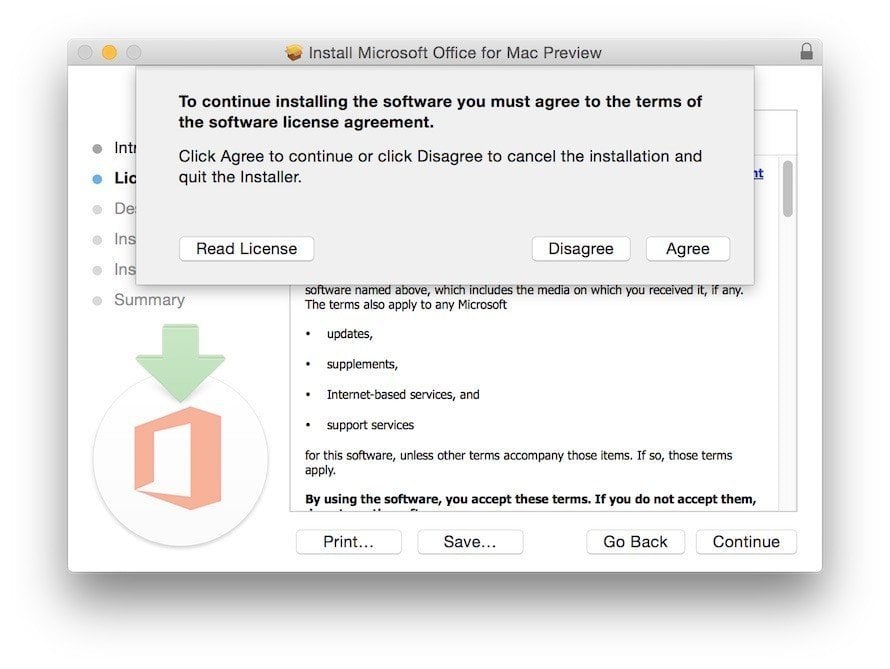
If your SaaS application has a desktop component, then you could implement clickwrap for the desktop app's Terms agreement during installation of the app.
The installation process for Microsoft Office for Mac includes a popup box that states that "to continue installing the software you must agree to the terms of the software license agreement." If you click the "Disagree" button, the installation will be cancelled and the program will be closed:
The Garmin Express Software app requires users to agree to Garmin's Terms and Conditions agreement for that application before being able to install the application and download the map updates.
Notice how the "Continue" button is greyed out until the "I accept the agreements" box is clicked. Then, the "Continue" button becomes active and clickable. This is another example of making sure that the user cannot continue installing the software unless the expressly agrees to accept the legal agreements.
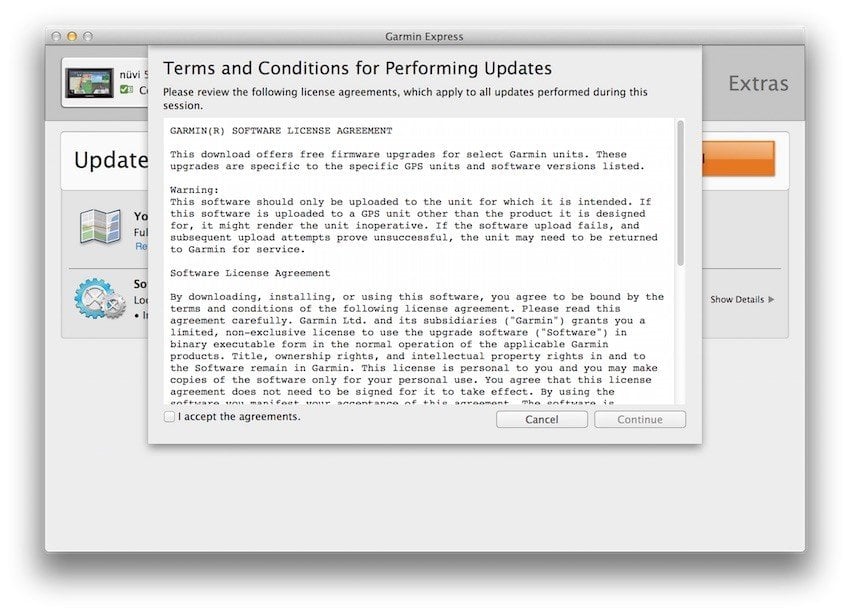
Additionally, you need to keep a record of the consent users provide to be able to prove you have it if necessary.
If you update your Terms and Conditions, in some cases you may need to get fresh consent. Here's a way you can do this with clickwrap:
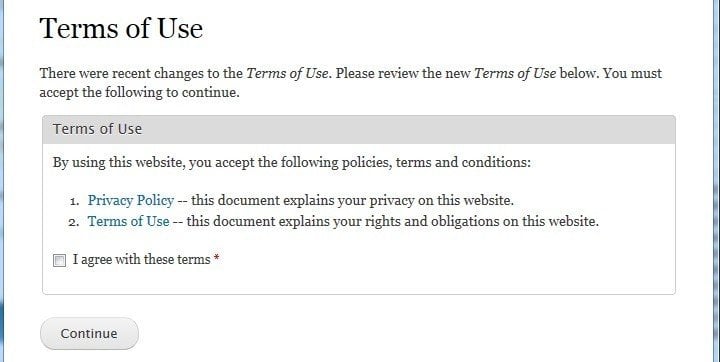
You can see that both the Privacy Policy and Terms of Use agreement are hyperlinked to (so the user can easily find and read the documents), and the check box is directly below the legal documents that are hyperlinked.
It's clear that by clicking "I agree with these terms" the user is agreeing to both the Privacy Policy and Terms of Use agreement linked.
Getting Agreement: Accounts Created on Website, Not via App
Most SaaS businesses utilize a website and also offer a mobile app that users can download to increase productivity and mobility.
Usually, so long as you obtain active acceptance from your customers in one medium (such as your website when they create the account to log in to the mobile application), using the browsewrap method in other mediums (the mobile application) means that you still have valid consent from users.
However, it's recommended to implement clickwrap whenever possible, at the entry point of each medium that your application uses.
Some SaaS businesses will require a user to have already signed up through the main website, and then only offer a login option on the mobile app with no option to create an account from the mobile application. In this case, the website is the only medium to implement the clickwrap method of getting the user to agree to terms and rules that will also cover the mobile app usage.
Consider the SalesForce mobile app.
When a user first downloads and opens the app, the EULA acceptance screen pops-up, and a user must accept the terms of the EULA in order to use the mobile app.
This EULA agreement is specific for the mobile version of SalesForce. EULA agreements are different from Terms and Conditions agreements.

After accepting the EULA, users are then taken to a login screen. In order to log in and use the app, a user must have an already-created login name and password. There's no option for creating a SalesForce account through the mobile app:
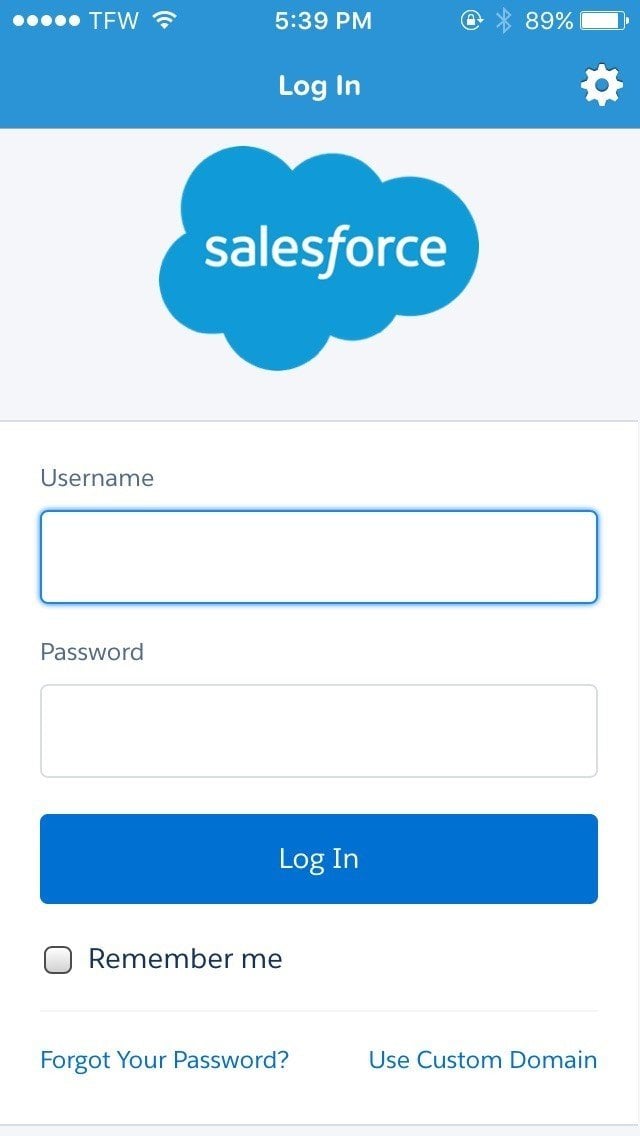
For a user to create a SalesForce account, the user must do so through the SalesForce website where the clickwrap method is in place for getting users to agree to the terms of the legal agreements.
It's recommended to implement the clickwrap method at the place where your users will register for an account:
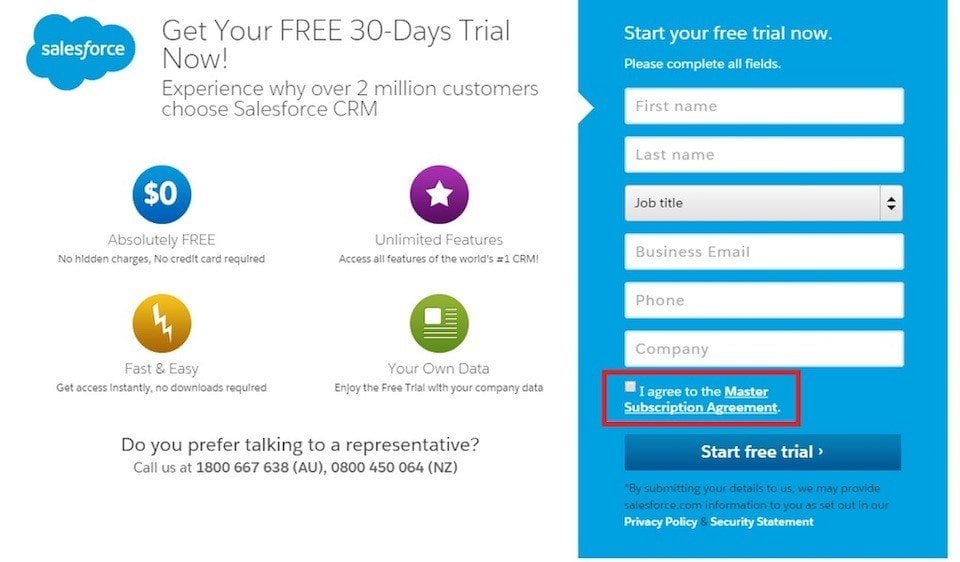
Summary of a SaaS Terms and Conditions Agreement
As a SaaS business owner, you must be sure that your Terms and Conditions agreement is easily accessible on all of the company's digital properties.
The way in which you present this contract sets the tone for how users interact with your products. It also helps ensure they know what they can do with it before downloading or signing up for any service, so there are no surprises down the line.
Crafting a Terms and Conditions agreement is an important step to take as part of running your business, so remember to use clauses specific to your SaaS service or product, make them easy-to-read, informative, and concise. And, always get explicit agreement to make your Terms and Conditions legally binding.
In conclusion, when you're ready to begin crafting your own customized SaaS Terms and Conditions agreement, we invite you to view our sample agreement or use our Terms and Conditions Generator to get the ball rolling.
After you have created your Terms and Conditions agreement, make sure to review them every few months to ensure that they are current.
Download Sample SaaS Terms and Conditions Template
Generate Terms & Conditions in just a few minutes
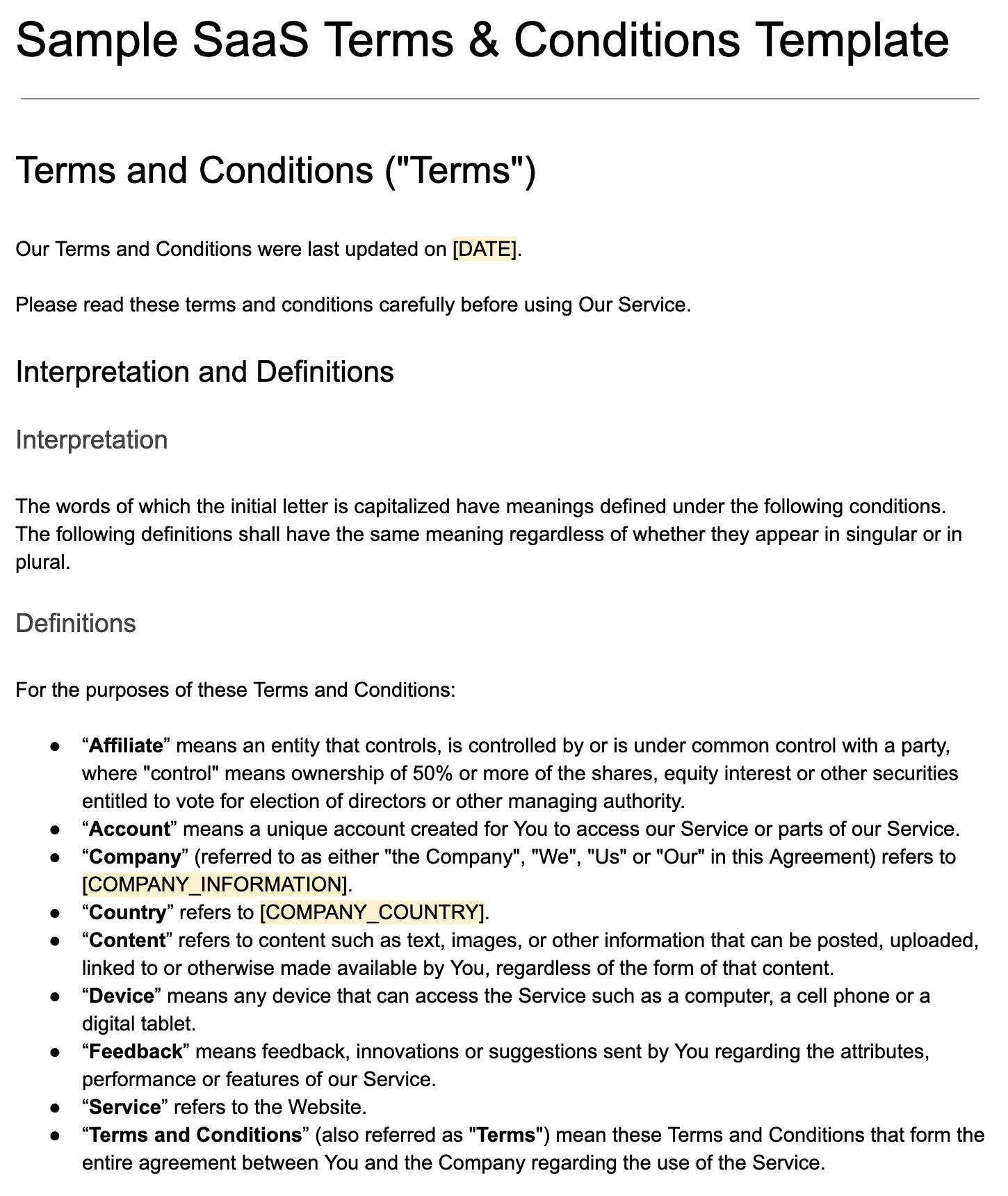
This free Sample SaaS Terms and Conditions Template is available for download and includes these sections:
- Introduction
- Definitions
- Acknowledgment
- User Accounts
- Content
- Copyright Policy
- Intellectual Property
- User Feedback
- Links to Other Websites
- Termination
- Limitation of Liability
- "AS IS" and "AS AVAILABLE" Disclaimer
- Governing Law
- Disputes Resolution
- Severability and Waiver
- Changes
- Contact Information
Sample SaaS Terms and Conditions Template (HTML Text Download)
You can download the Sample Terms and Conditions Template as HTML code below. Copy it from the box field below (right-click > Select All and then Copy-paste) and then paste it on your website pages.
Sample SaaS Terms and Conditions Template (PDF Download)
Download the Sample SaaS Terms & Conditions Template as a PDF file
Sample SaaS Terms and Conditions Template (Word DOCX Download)
Download the Sample SaaS Terms & Conditions Template as a Word DOCX file
Sample SaaS Terms and Conditions Template (Google Docs Download)
Download the Sample SaaS Terms & Conditions Template as a Google Docs Document
More T&Cs Templates
More specific T&Cs Templates are available on our blog.
| Sample Terms and Conditions Template | A Terms and Conditions agreement for all sorts of businesses. |
| Sample Mobile App Terms and Conditions Template | A Terms and Conditions agreement for mobile apps. |
| Small Business Terms & Conditions Template | A Terms and Conditions agreement for your Small Business. |
| Sample Ecommerce Terms & Conditions Template | A Terms and Conditions agreement for your Ecommerce Store. |
| Sample EULA Template | An End-User License Agreement for mobile apps. |

Comprehensive compliance starts with a Privacy Policy.
Comply with the law with our agreements, policies, and consent banners. Everything is included.