If you don't have a Privacy Policy when one is required, you will be violating privacy laws. The penalties for violating these laws includes expensive fines that can hurt your bottom line.
In this article, we will consider why business owners need a Privacy Policy and what fines and penalties they can expect if they don't have one.
We'll also provide some tips on creating a Privacy Policy that meets legal requirements.
Our Privacy Policy Generator makes it easy to create a Privacy Policy for your business. Just follow these steps:
-
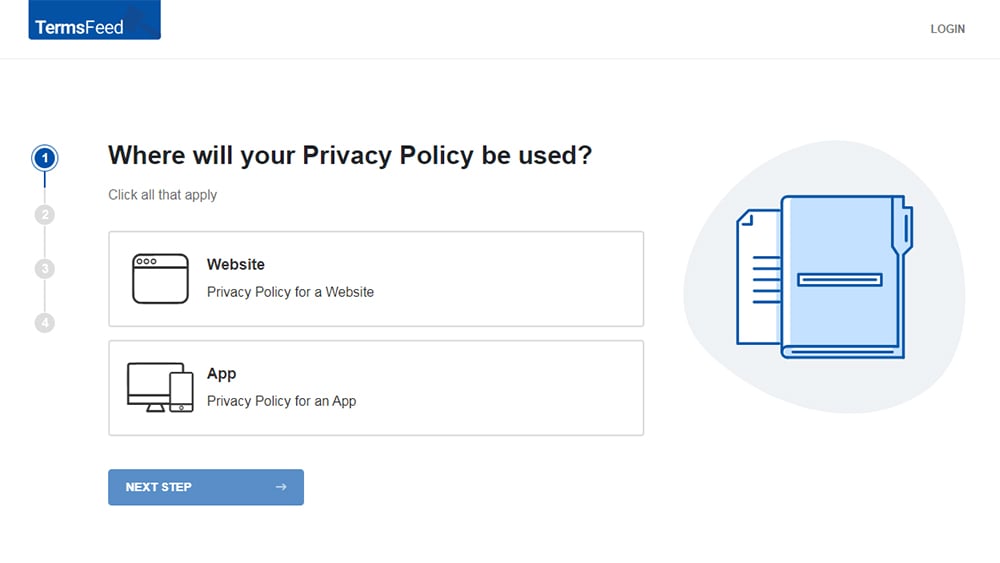
At Step 1, select the Website option or App option or both.
-
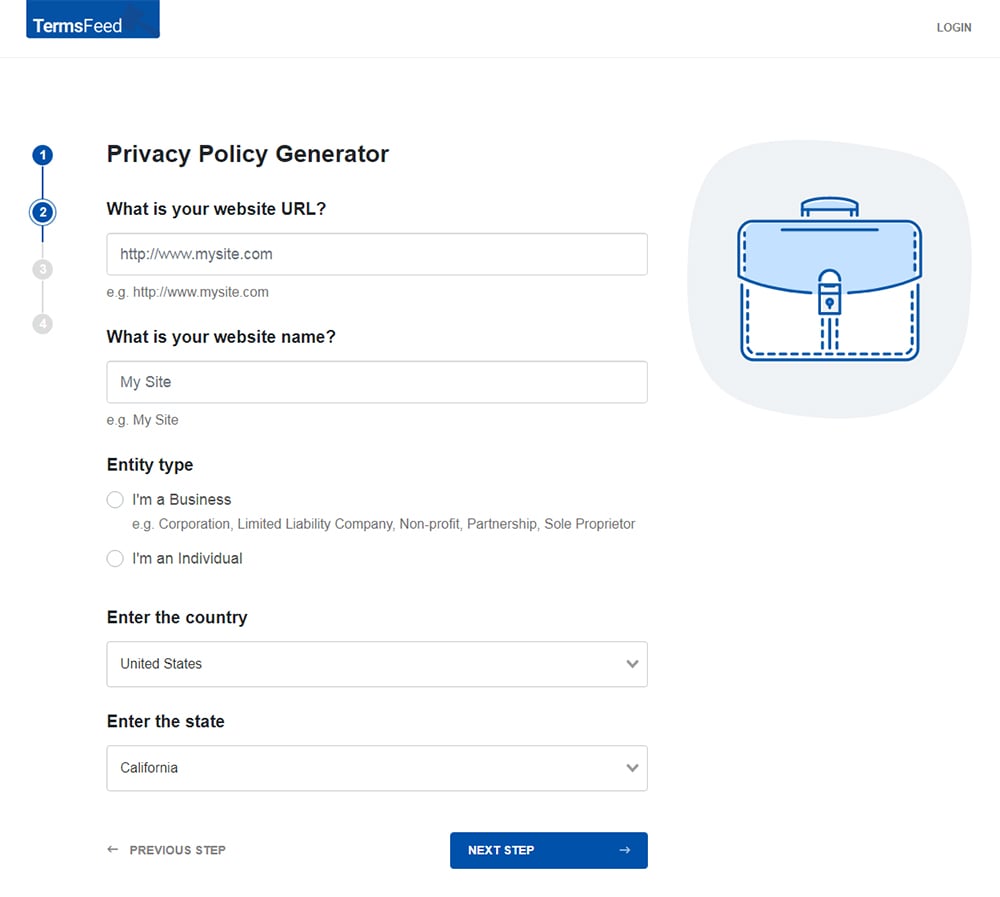
Answer some questions about your website or app.
-
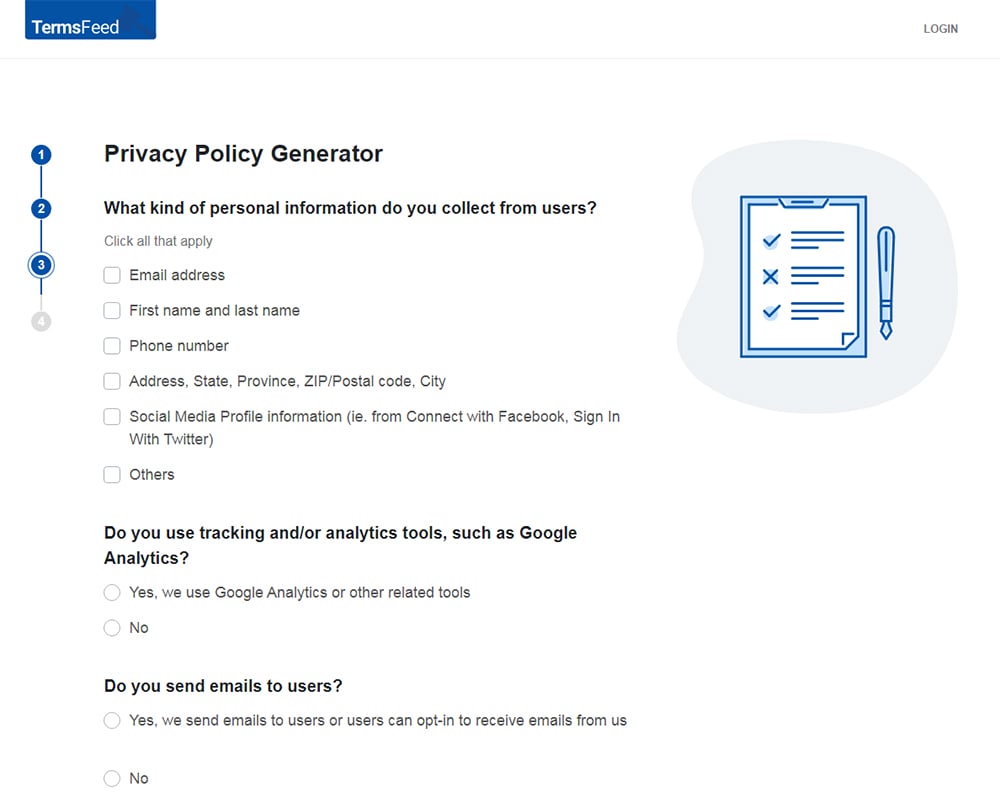
Answer some questions about your business.
-
Enter the email address where you'd like the Privacy Policy delivered and click "Generate."
You'll be able to instantly access and download your new Privacy Policy.
What is a Privacy Policy?
A Privacy Policy is a legal document that discloses how a company collects, uses, discloses, and secures a customer or client's personal information. It fulfills a legal requirement to protect consumer privacy.
A Privacy Policy should be easily accessible so that customers and clients can find and read it at their convenience, at any time. It must also be written in language which is clear and concise, that the average person can understand.
The contents of a Privacy Policy will vary depending on the country in which the business operates and the type of business. However, you should include certain elements in every Privacy Policy.
These include:
- The kinds of personal data collected by the business
- How you will use the personal data
- Whether you will share the personal data with third parties
- The process for opting out of having their personal data collected or used
- How the customer or client can access their personal data
- The contact details of the business in case the customer or client has any questions or concerns about the Privacy Policy or business practices
Businesses that do not have a Privacy Policy are at risk of being fined by government agencies. Additionally, customers who feel their privacy rights have been violated can sue your company.
Companies need to understand the privacy laws in the regions where they do business, and the fines and penalties associated with non-compliance with such laws.
Examples of Companies Fined for Non-Compliance with Privacy Laws

Many business owners don't understand the gravity of violating existing privacy laws such as the EU's General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) or California's Online Privacy Protection Act (CalOPPA). However, the cost to a company for non-compliance can be staggering.
Here are ten examples of well-known companies fined for privacy law violations over the last few years:
- In 2018, Facebook was fined £500,000 in the UK for failing to protect user data from being harvested by Cambridge Analytica. The UK also found the company to have misled investigators about the extent of the problem.
- In 2018, British Airways was fined $26 million for a data breach. Courts upheld the authority's position that British Airways failed to have appropriate security measures, which could have prevented the breach.
- In 2019, Google was fined $57 million for what French regulators called a lack of clarity and transparency in how it informed users about how it handled personal data and for failing to gain consent for personalized ads.
- In 2019, Equifax was fined $575 million by the U.S. Federal Trade Commission (FTC) for failing to protect over 147 million customers' personal information adequately.
- In 2020, H&M was fined $41 million for violating the privacy of their employees.
- In 2020, the Marriott was fined $23.8 million. Like British Airways, Marriott's data was not secured properly. Hackers were able to break in and expose the records of 383 million guests.
- In 2021, Amazon was fined a colossal $877 million due to GDPR violations involving cookie consent.
- In 2022, Facebook was fined $68 million for violations of the GDPR's cookie consent requirements.
- In 2022, Clearview AI was fined $20.5 million by the Italian data protection authority for privacy violations related to the company's facial recognition products.
- In 2022, Facebook once more made the list as a privacy violator, with Meta Ireland being fined $18.6 Million for failing to demonstrate that it had implemented proper security following over 18 breaches.
Let's take a look at a few of the most widely-applicable privacy laws and what the fines are for violating each of them.
Fines for Violating CalOPPA

The California Online Privacy Protection Act (CalOPPA) is a piece of legislation designed to protect users' online personal information. This U.S. law from the state of California requires commercial website owners to include a link to the business Privacy Policy so that users can know how these companies will use their data.
To comply with CalOPPA, companies must have a Privacy Policy that includes certain information, and take reasonable steps to ensure that the Privacy Policy is accurate and up-to-date.
The law applies to any company that collects California residents' personal information, regardless of whether the company is based in California.
CalOPPA defines personal information as "information that identifies, relates to, describes, or is capable of being associated with, a particular individual."
This includes things like:
- A person's name
- Physical address
- Email address; and
- Phone number
It also includes persistent identifiers like cookies and IP addresses.
When a company violates CalOPPA, it can face severe fines. CalOPPA violations are considered unfair business practices under the California Unfair Competition Law (UCL).
The UCL forbids businesses from engaging in any practices that are seen as unfair, unlawful, or fraudulent. Any violation can result in civil penalties of up to $2,500.
In order to ensure compliance with CalOPPA, companies should regularly review their privacy practices and update their Privacy Policy as necessary.
There are also some clauses your CalOPPA-compliant Privacy Policy should include.
They are:
- A clause that provides information on the types of personal information you collect, why you collect it, and with which third parties you share it (if any).
- A clause that lets users know how they can have their personal information changed or deleted.
- A clause that lets users know how you will inform them of changes made to your Privacy Policy.
- A clause that provides users with information on how you will respond to Do Not Track requests.
- The effective date of your Privacy Policy, and/or last updated date.
You can use our CalOPPA Privacy Policy Template to create your own if you don't have one.
Fines for Violating COPPA

The Children's Online Privacy Protection Act (COPPA) is a United States federal law. The FTC has enforcement authority over COPPA compliance and has brought numerous actions against website and app operators for violating the law.
The goal of COPPA is to ensure the security and privacy of any personal data collected from individuals under the age of 13.
According to COPPA, personal data includes but is not limited to:
- A child's name
- Physical address
- Phone number
- Email address
COPPA requires businesses to:
- Notify parents or guardians about their data collection practices
- Obtain parental consent before collecting personal information from children (with some exceptions), and
- Take reasonable measures to protect children's personal information from unauthorized access or disclosure
Businesses that violate COPPA can be subject to civil and criminal penalties. Currently, the maximum civil penalty is $42,530 per privacy violation per child.
There are some important steps companies can take to ensure they comply with COPPA. These include:
- Designating someone at the company to be responsible for compliance with COPPA
- Reviewing their website and online services to identify any areas where personal information is collected from children
- Putting in place policies and procedures to secure children's personal information
- Training employees on these policies and procedures
- Keeping records of their efforts to comply with COPPA
Businesses can help protect children's online privacy by taking these steps while avoiding costly fines and penalties.
Use our COPPA Privacy Policy Template to help you create a compliant Privacy Policy today.
Fines for Violating the EU Cookies Directive

The EU Cookies Directive is a piece of legislation that the EU incorporated into the e-Privacy Directive.
The essential idea behind it is that companies now need to obtain user consent before placing cookies on their devices such as computers, laptops or smartphones.
Cookies are small files that get embedded on your device when you visit a website. They are used for various purposes like remembering your login details or tracking your browsing habits.
Companies that collect personal data through cookies must provide clear and concise information about their activities and ensure that users can easily give or withhold their consent. Failure to do so can result in hefty fines.
The Cookies Directive has been widely criticized for being too complicated and putting an undue burden on businesses. Nevertheless, it remains an integral part of EU legislation.
Violators can be subject to monetary fines of up to 500,000 GBP. This amount is only given in the case of a deliberate breach that brings about substantial distress to the data subject. In other cases, the maximum fine is much lower, at 100,000 GBP.
There are a few crucial things that companies need to do to comply with the Directive.
First, ensure that your company has a Privacy Policy or Cookies Policy that provides clear and concise information to visitors about the cookies that are being used on the website. This includes specifying the purpose of the cookies and obtaining consent from visitors before storing or retrieving any information.
Second, companies must ensure that they have implemented appropriate technical and organizational measures to protect user data. Part of that is ensuring that only authorized personnel have access to cookie data and that all data is securely stored.
Finally, companies should keep detailed records of their compliance with the Directive, including information about the cookies used on their website and how they obtained consent from visitors.
These records should be made available upon request to authorities or individuals who exercise their right to access their personal data.
Fines for Violating the GDPR

The General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) has been a game-changer for how businesses protect the data of their customers and users. The EU created it in response to the awareness that people have become increasingly comfortable sharing their personal information online without understanding the implications.
The GDPR is designed to give individuals more control over their data, and to hold businesses accountable for failing to safeguard it.
The main principles of the GDPR are that companies must only collect data for specific, explicit, and legitimate purposes, and that the data must:
- Be accurate and up to date
- Not be retained for a longer period than is required, and
- Be processed in a way that ensures appropriate security
People who are protected by the GDPR are also given a number of user rights that must be facilitated.
The GDPR sets out the maximum administrative fines the EU can impose on companies for breaching the law. These fines are tiered, with the second tier being the most serious breaches.
The maximum fine that can be levied for a first-tier breach is 10,000,000 EUR, or up to 2% of the total worldwide annual turnover of the preceding financial year, whichever is higher.
These GDPR fines are significantly higher than the maximum fine under the previous data protection regime, which was 500,000 EUR.
Tier two fines max out at 20,000,000 EUR or 4% of the total yearly sales for the preceding fiscal year, whichever is higher.
In determining the fine amount, the GDPR considers the infringement's nature, gravity, and duration, the number of data subjects impacted, and the level of damage they suffered. The Regulation also provides for a series of aggravating and mitigating factors that may be considered when setting the fine level.
To comply with the GDPR and avoid violations, the law requires businesses to take a number of steps to protect the personal data they hold.
These include but aren't limited to:
- Ensuring that personal data is collected and processed lawfully, transparently, and in a fair manner
- Collecting only the personal data that is required for the purposes for which it is to be used
- Ensuring that personal data is accurate and up-to-date, and
- Ensuring that personal information is kept for no longer than is necessary
A business needs to include several clauses in its Privacy Policy to ensure compliance with the GDPR.
These include:
- The types of personal data that are collected and processed by the business
- The purposes for which the personal data is used
- How long the personal information will be stored
- Who has access to the personal data, and
- What rights customers have with regards to their private data
Create a GDPR-compliant Privacy Policy today using our template.
Fines for Violating PIPEDA

The Personal Information Protection and Electronic Documents Act (PIPEDA) is a Canadian federal law that sets out how organizations must handle the personal information of Canadians.
It establishes guidelines and rules regarding how organizations collect, use, and disclose personal information.
PIPEDA protects four primary consumer rights. These are:
- The right to know why an organization is collecting, using, and disclosing an individual's personal information
- The right of the consumer to access the personal information that an organization has about them
- The right to ask for a correction of any errors in that personal information, and
- The right to file a complaint if a consumer feels that their privacy rights have been violated
If an organization is found to be knowingly in breach of PIPEDA requirements, it can be fined up to $100,000 for each violation.
Business owners can take a few simple steps to ensure they are compliant with PIPEDA.
First, they should appoint a privacy officer responsible for ensuring the organization complies with PIPEDA requirements.
Second, they should develop policies and procedures to protect personal information and train all employees on these policies and procedures.
Finally, they should regularly review their Privacy Policy and privacy practices to ensure they remain compliant with PIPEDA.
Our Sample PIPEDA Privacy Policy Template can help you get compliant today.
Summary
Business owners need to keep up with privacy legislation. Failure to do so could harm your company's bottom line. You need to be aware of several different data privacy laws, and it's essential to understand any amendments that have been made to them.
Some of the most widely applicable privacy laws include CalOPPA, COPPA, the EU Cookies Directive, the GDPR, and PIPEDA. These laws regulate how companies collect, use and disclose personal data, and failure to comply can result in heavy fines.
That's why it's critical for companies to invest in privacy compliance. By doing so, they can avoid costly penalties and create a foundation for protecting their customers' privacy.
A great way to begin ensuring compliance is to have a well-written, accurate, and easy-to-understand Privacy Policy on your company's website.

Comprehensive compliance starts with a Privacy Policy.
Comply with the law with our agreements, policies, and consent banners. Everything is included.